The Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) certification is a globally recognized credential in the field of information security. The CISSP exam covers eight domains that form the Common Body of Knowledge (CBK). This post provides a detailed overview of these domains and their weightings in the exam.
The 8 CISSP Domains and Their Weightings
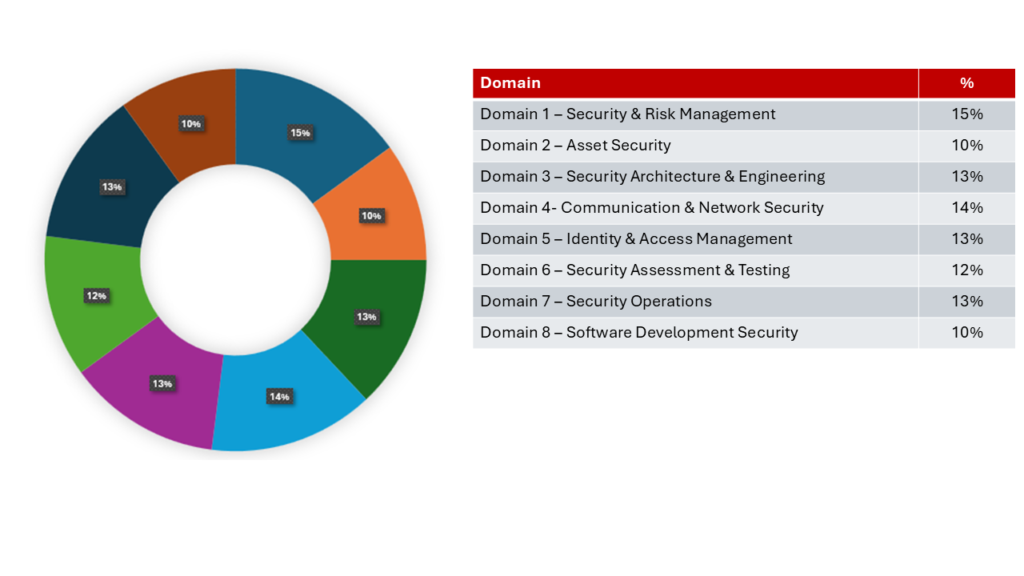
- Security and Risk Management (15%)
- Asset Security (10%)
- Security Architecture and Engineering (13%)
- Communication and Network Security (14%)
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) (13%)
- Security Assessment and Testing (12%)
- Security Operations (13%)
- Software Development Security (10%)
Domain Highlights
Security and Risk Management
This domain covers risk identification, assessment, information security governance, compliance, and professional ethics
Asset Security
Focuses on identifying, classifying, and protecting an organization’s assets, particularly information assets.
Security Architecture and Engineering
Includes concepts related to system architecture, design, and implementation of secure systems
Communication and Network Security
Covers network infrastructure, protocols, and secure communication methods.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Deals with authentication, authorization, and access control systems
Security Assessment and Testing
Involves security testing methodologies, vulnerability assessment, and risk analysis
Security Operations
Focuses on day-to-day security operations and incident management
Software Development Security
Covers secure coding practices and software development lifecycle security
Conclusion
Understanding these domains is crucial for CISSP candidates and information security professionals. The CISSP certification validates a professional’s knowledge across these critical areas, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of information security principles and practices.